Exercise is great for kids.
Kids who exercise are healthier and stronger. Being overweight or obeseThey are better Physical and Mental Healthand their performance in the classroom improved. Exercising as an adult.
So the more you exercise now the better. But what about weight training? If you’ve spent any time looking through the comments sections of social media posts about kids lifting weights, you know there’s a fierce debate brewing about whether it’s safe for kids.
Unfortunately, there are still many misconceptions about weight training and children. Research shows that weight training is safe if you follow a few common sense precautions.
Common misconceptions
Weightlifting is an example of “resistance training,” which also includes bodyweight training, weightlifting, jump training, and even sprinting.
A common misconception is that strength training is bad for kids.
You may have heard that it stunts growth, but this rumor is not backed up by scientific evidence.
Concerns about stunted growth arise because children may develop a condition called “growth plate injury.” Growth plates are pieces of cartilage at the ends of bones that help them grow. These plates turn into bone when bones stop growing during puberty.
Damage to the growth plates can cause bones to close prematurely, resulting in shortened limb length and stunted bone growth.
These injuries Can happen to childrenHowever, most often it occurs during impact-related injuries during sports or falls.
actual, No evidence Unsupervised strength training programs can stunt a child’s growth and damage their growth plates.
The load on the body is similar to that of strength training. Jumping and landingwhich is something all kids do. Plus, there’s a much lower risk of injury with strength training than with many other forms of exercise. Recreational and sporting activities.
Nomad_Soul/Shutterstock
What are the benefits of weightlifting for kids?
Strength training is good for children Physical StrengthThese include strength, power, speed, agility and endurance.
Strength training is also beneficial for: Overweight or obese children People who don’t want to or can’t do aerobic exercise like running or swimming.
Strength training also benefits children’s physical and mental health. For example: Metabolic Healthhelp manage WeightRelieving symptoms Depression and anxietyImprove Self-esteemand help Academically.
How old is too early to start weightlifting?
There is no minimum age to start, but participants must be able to follow instructions and safety rules. Kids who are ready for sports are usually ready to do some type of strength training as well.
Both World Health Organization (WHO) and Australian Government It recommends 60 minutes of exercise per day for children ages 5 to 17. It also encourages kids to exercise at least three days a week to strengthen their muscles and bones.
Many forms of exercise build muscle and bone strength. This includes high-intensity sports, outdoor activities like climbing, jumping and running, and of course strength training.
That means kids don’t necessarily have to be lifting weights, as long as they do some other type of exercise.
However, very few children meet these guidelines.
According to Australian data, One in four (about 23%) Percentage of children ages 5 to 14 who get enough physical activity.
The number is about 6% of older children aged 15 to 17.
This suggests that adding formal exercise to a child’s daily routine is a good thing.
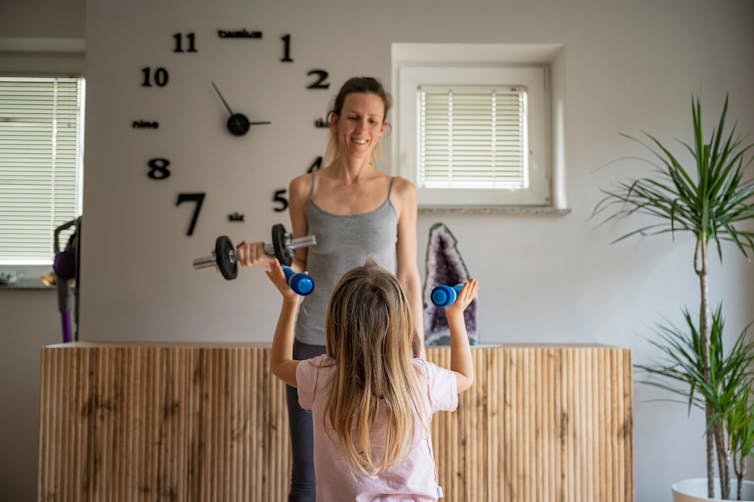


Gajus/Shutterstock
How should your child begin resistance exercise?
The key is to start slow and have fun.
The goal is to get kids to enjoy strength training and keep it going for life. success.
For younger elementary school children, the focus should be on balance, coordination, agility and endurance.
This means playing games that involve running and chasing, and activities that build muscular endurance (such as climbing, carrying and pushing).
To teach children how to move, you can also incorporate bodyweight exercises such as push-ups, pull-ups and planks.
In the upper elementary years, kids can get more targeted training, which might include more bodyweight exercises, jumping exercises like hurdles and skips, and even light weight exercises like squats and bicep curls.
Finally, once you reach high school, you can try more formal weight training exercises using moderate weights, such as lunges, deadlifts, presses, and rows.
As you gain confidence, try lifting heavier weights.
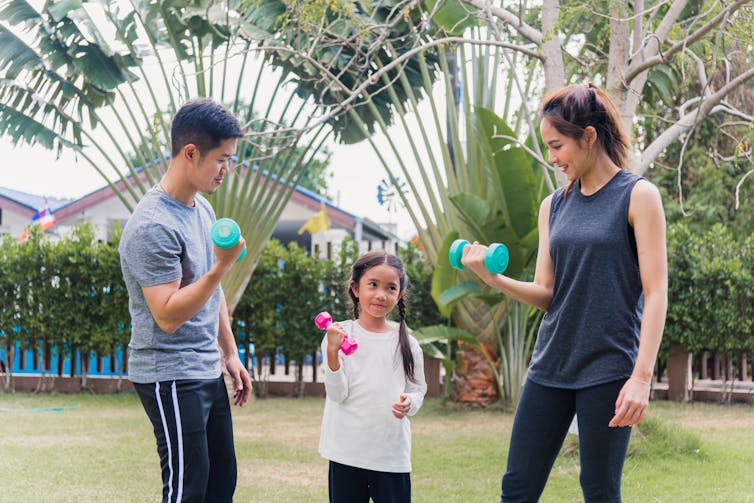
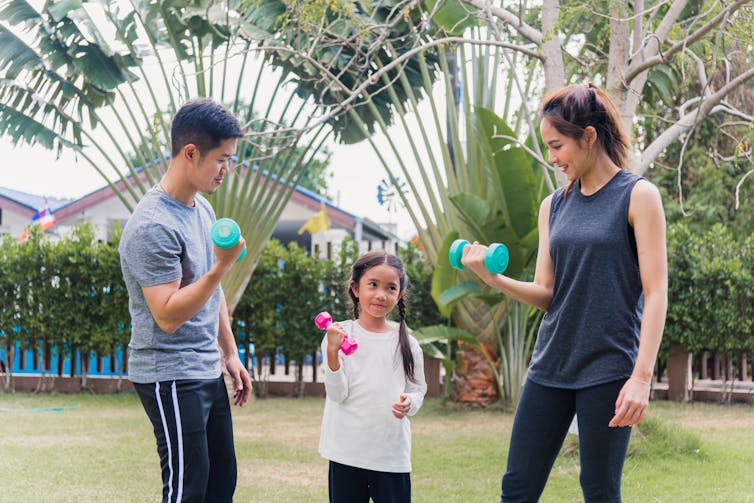
Sorapop Udomsri/Shutterstock
What do parents need to know?
First, strength training is relatively Lower risk of injury Under proper supervision.
Proper supervision means adults teaching children proper technique and making sure they don’t fall into the trap of trying to impress their peers.
Second, start with light weights. For beginners, lifting light weights for about 10 to 15 repetitions (or “reps”) will help you: Similar effects to lifting heavy weights Once you’ve done it a few times it will probably be safer.
Lifting lighter weights and doing more repetitions has another benefit: it allows kids to practice and improve their technique.
Finally, don’t be afraid to get involved. Adults benefit greatly. From strength trainingtoo.
Why not make the most of it and get involved?

