Most of us have heard the advice to drink 8 cups of water a day, but there is some flexibility and you can drink too much or too little. The latter is more common.
Most of us have heard the advice to drink 8 cups of water a day, but there is some flexibility and you can drink too much or too little. The latter is more common.
Drinking too little can lead to dehydration, which can lead to a range of symptoms from dizziness to death in the worst cases. Excessive drinking can also have potentially dangerous effects, experts say, because too much water in the body affects the electrolyte balance in the body. They shared advice on how much a person should drink, the signs someone is drinking too much water, and whether the right balance exists for the average water drinker.
How much water should you drink in a day?
As for how much to drink, 8 glasses is a guideline, but people also take in water from food and other drinks. About 20% of your daily water intake normally comes from food. According to the US National Academy of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, an adult male living in temperate climates should drink about 15.5 cups of fluid per day, including water, other drinks, and food. An adult woman living in a temperate climate with moderate annual temperatures should drink about 11.5 cups of water per day. Women should drink more during the day if they are menstruating, pregnant or breastfeeding.
The amount of water also depends on the climate and season. On a hot day, much of the water that a person ingests is expelled through perspiration as the body cools down. The average person has 2.6 million sweat glands and loses water and electrolytes when he sweats.

Drinking enough water and getting enough electrolytes keeps your body functioning properly. Dehydration can cause dizziness, confusion, fatigue, and extreme thirst. It can cause more serious symptoms such as heat exhaustion, heat stroke, seizures, and kidney failure.
Is it okay to drink too much?
yes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advises people not to drink more than 48 ounces, or 6 cups, per hour. Drinking large amounts of liquids, such as water and sports drinks, can cause an emergency because the salt levels in the blood become too low.
When this happens, water levels in the body rise and cells swell, which can cause health problems as the body tries to regulate electrolyte levels, says New York Presbyterian Westchester Hospital Emergency Department. said Dr. Mahesh Polavarap, medical director of
“If you have too much water, you’re basically pushing that water into your cells to balance sodium and other electrolyte concentrations,” Polavalup says. “When that happens, brain cells and other cells in the body start to swell.”
Health experts told CBS that drinking too much is not a common problem and that the average healthy adult should focus on staying hydrated.
“This is nothing to worry about. You should drink as much water as you feel you need,” says Polavalap.
Experts say overhydration is common in endurance athletes, in people with kidney problems, and in people taking certain medications that can cause excessive thirst, such as antidepressants and diuretics. are seen more frequently. Older people are at greater risk because age-related declines in overall organ function may increase vulnerability to overhydration.
What are the signs of drinking too much water?
This is where things get tricky, says Jason Ewalt, R.D., Mayo Clinic. Many of the symptoms of overhydration can be confused with dehydration. Both can cause nausea, muscle spasms, and fatigue. There are several important ways to tell the difference.
“Watching your thirst and urine color is the easiest way to limit the chances of both overhydration and dehydration,” says Ewoldt.
If you feel thirsty, you may need to drink more water. Dark yellow urine is also a sign to drink more.
Clear urine is a sign that you may need to feel better and lose fluids.
What happens when you drink too much water?
Too much water causes a condition called hyponatremia, which occurs when the salt concentration in the body is too low. Also known as “water poisoning”. Drinking large amounts of water in a short period of time can upset the body’s electrolyte balance.
If someone drinks too much, the kidneys may not be able to keep up and excrete the excess fluid.
“If you drink too much pure water, the solutes in your body need to be dispersed more in space, and you can develop electrolyte disturbances that can cause serious problems in your brain, or you can have seizures,” he said, working as a professor. says Dr. David Metz. said a doctor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine.
Other symptoms of hyponatremia include nausea, vomiting, headache, altered mental status/confusion, fainting, lethargy, and coma. In extreme cases, it can even lead to death.
In a 2007 incident, a 28-year-old Jennifer StrangeA Californian mother of three, she died of acute water poisoning after participating in a water drinking contest. The radio station had participants compete to see who could drink the most water without using the toilet. At the time of the incident, one of Strange’s colleagues said the victim “told one of our bosses that on her way home her head hurt so much…she was crying and that was the last time.” ‘ said. she heard from her “
17 years old soccer player died In 2014 in Georgia, I drank two gallons of water and another two gallons of Gatorade during practice.
How can you safely drink water when it’s hot?
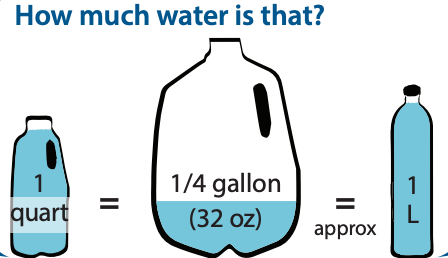
drink before you get thirsty, CDC recommends. If you are working outside in the heat, drink about 1 cup of water every 15-20 minutes. This equates to 3/4 to 1 quart (24 to 32 ounces) per hour. Drinking frequently is more effective for rehydration than drinking frequent small amounts.
“People think thirst is what makes them want to drink water, but thirst is a late sign of most dehydration, so don’t wait for it to happen,” Polavarap says. says.
According to the CDC, it’s important to drink water to replace fluids lost through sweating, but it’s also important to eat regular meals to replace the salts lost through sweating and maintain electrolyte balance.
© 2020 CBS Interactive Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.