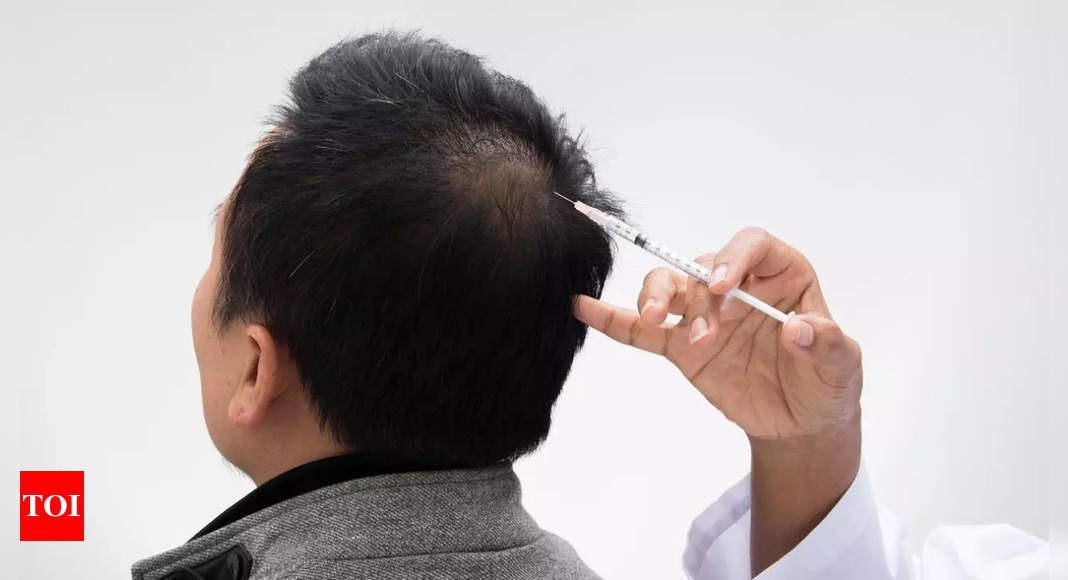
Some of the world’s greatest inventions were discovered by chance.
A revolutionary hair loss treatment was discovered by chance by researchers while studying the effects of naturally occurring plants. deoxyribose sugar For wound healing in laboratory mice. They were delighted to discover that administering the sugar caused the mice to rapidly grow fur around the lesions, prompting the scientists to investigate further. This led to the discovery of a cure for hereditary hair loss that affects men and women around the world.
By chance, researchers applied sugar to the wounds of laboratory mice and noticed that the fur around the wound quickly regenerated. The study was published in Frontiers in Pharmacology in July of this year.
Scientists from the University of Sheffield and Pakistan’s COMSATS University were studying the ‘deoxyribose’ moiety of deoxyribonucleic acid, a sugar that occurs naturally in the body and helps form DNA.
When they made this surprising observation, they were studying how these sugars heal wounds in mice when applied topically, and the fur surrounding the lesions in mice was untreated. They discovered that they grow faster than mice.
To study this further, they took male mice that had been depilated by testosterone and had the hair removed from their backs. Every day they applied a small amount of deoxyribose sugar gel to exposed skin. Within a few weeks, the fur in the area where the gel was applied showed “robust” regrowth, with long, thick, individual hairs.
In fact, deoxyribose gel was found to be so effective that researchers concluded that deoxyribose gel is just as effective. minoxidilcommonly known by the brand name Rogaine, is a topical hair loss treatment.
Sheila McNeil, a tissue engineer at the University of Sheffield, said: “Our research shows that the answer to hair loss treatment could be to use the naturally occurring sugar deoxyribose to boost blood supply to the hair follicles and stimulate hair growth. “It suggests that it could be as simple as facilitating.”
hereditary alopeciaalso known as male pattern baldnessis a common cause of hair loss caused by a combination of genetics, hormones, and aging. This disorder affects up to 40 percent of the population. Two drugs are approved to treat hair loss.
The over-the-counter treatment minoxidil slows hair loss and promotes hair regrowth, but it doesn’t work for everyone. Male patients can consider finasteride (Propecia), a prescription drug that slows hair loss in 80 to 90 percent of cases.
However, they must be taken continuously and can cause side effects such as erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, depression, testicular pain, and breast pain. Finasteride is not approved for women.
“Treatment of male pattern baldness remains difficult,” McNeil and colleagues, led by COMSATS biomaterials researcher Muhammad Anjum, wrote in a published paper.
Sugar gel is as effective as minoxidil
Researchers developed a biodegradable, non-toxic gel made from deoxyribose and tested it in a mouse model of androgenetic alopecia. Minoxidil was also tested separately, and some mice received a combination of sugar gel and minoxidil. Mice given the deoxyribose gel showed new hair follicle growth compared to mice given the gel without the active ingredient.
Both minoxidil and sugar gel were found to promote 80 to 90 percent effectiveness. hair regrowth However, in mice with androgenetic alopecia, the combination of treatments did not make much of a difference.
How can it help treat hair loss in humans?
Researchers weren’t sure exactly how deoxyribose gel worked on hair growth, but they found that deoxyribose gel led to longer, thicker hair growth in mice and increased blood vessel and skin growth around the treatment area. I noticed an increase in cells.
“The better the blood supply to the hair bulb, the larger the diameter of the hair bulb and the growth of more hair,” the researchers wrote.
This has raised expectations in the field of treating alopecia in humans and promoting hair, eyelash, and eyebrow regeneration after chemotherapy.
“This area is poorly researched and new approaches are needed,” the authors write.
The research could be advanced by experimenting with female mice, which suffer from alopecia, similar to the promising results shown in male mice.
Reasons behind hair loss:
Hair loss can have many different causes, including:
Genetics: The most common cause of hair loss is a genetic disorder called androgenetic alopecia, which usually occurs gradually and in a predictable pattern.
Hormonal changes: Hair loss can be caused by hormonal changes due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or thyroid problems.
Medications and supplements: Hair loss can be a side effect of certain medications used for cancer, arthritis, depression, heart disease, gout, high blood pressure, and more.
Stressful events: Many people experience general hair thinning several months after a physical or emotional shock.
Hairstyles and treatments: Hairstyles that pull your hair too hard, such as braids, hair extensions, and tight ponytails, can cause hair loss.
Fungal infection: Tinea capitis, also known as tinea capitis, is a fungal infection of the scalp that is a common cause of hair loss in children.
Nutrient deficiencies: Hair loss can occur if you don’t get enough iron, protein, zinc, folic acid, vitamin D, or vitamin B12.
Poisoning: Slow poisoning with arsenic, thallium, mercury, lithium, or large doses of warfarin can cause hair loss.
Friction: Hair loss can occur when boots, socks, or tight clothing rub against your skin frequently.