Gout is the most common form of arthritis, affecting men three to four times more often than women.
An important scientific discovery has challenged the long-held notion that lifestyle variables such as diet and alcohol intake are the main causes of gout. According to research from the University of Otago, the development of gout is heavily influenced by genetics. By testing the DNA of millions of people, they discovered specific genes that increase the risk of developing gout. This groundbreaking discovery challenges conventional wisdom about gout and creates new opportunities to develop more powerful treatments and preventive drugs.
The research published in natural genetics It turns out that genetics are an important part of why some people get gout but most people don’t.
Lead author Professor Tony Merriman, from the University of Otago’s Department of Microbiology and Immunology, hopes the findings will help dispel some of the stigma surrounding gout.
“Gout is a chronic disease with a genetic basis and is not the patient’s fault. We need to break the myth that gout is caused by lifestyle and diet.” he said.
“This widespread myth creates shame for gout sufferers, with some suffering in silence and more likely not going to the doctor to receive preventative medication to lower uric acid levels in the blood and prevent pain. It will be.
“People believe that certain dietary factors, such as eating red meat, can trigger gout attacks, but the root cause is high uric acid levels, crystals in the joints, and the ability to ‘attack’ the crystals. You need to understand that it is a primed immune system. Genetics plays a role in gout. It plays an important role in all these processes. ”
This research has identified numerous immune genes and pathways that provide new targets and approaches to prevent gout attacks.
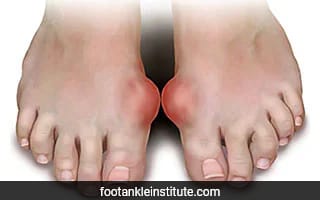
What is gout?
According to ankle research institute, Gout is a type of arthritis that affects the musculoskeletal system, also known as bones, joints, and muscles. It occurs when uric acid accumulates in the joints. When there is too much uric acid in the blood, it crystallizes in the joints, usually the big toe. The most common gout symptoms include redness, tenderness, swelling, and pain.