Scientists reversed diet-induced disease in obese mice and reduced the risk of side effects by administering drugs directly to the liver via nanogel carriers.
The research team believes that this new understanding of this mechanism means that encapsulating drugs in nanogels could be an efficient way to treat similar diseases such as fatty liver disease, type 2 diabetes and high cholesterol in the future. He says it means it is possible.
“100 million Americans suffer from obesity and related cardiometabolic disorders.” To tell S. Thai Thayumanavan, biomedical engineer and chemist at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, USA.
“We were very excited about this job.”
Nanogels deliver synthetic thyroid hormone drugs called thyromimetics.Thyroid Hormones Help Maintain Health liver metabolism balanced, but systemic thyroid hormone mimetics less effective, side effects.
“We realized we needed to selectively deliver this drug to the liver because it could cause complications if it went elsewhere.” explain Tayumanavan.
Using a mouse model, Thayumanavan et al. confirmed that carefully developed nanogel carriers with negatively charged (anionic) surfaces could be specifically directed to cells in the liver called hepatocytes.
“We came up with a very simple approach using our own invention, a nanogel that can be selectively directed to different targets,” said Tayumanabhan. To tell. “They were specifically designed to deliver hepatocytes to the liver.”
A thyroid hormone mimetic called axithyrome was packaged in anionic nanogels (ANGs) and administered daily to obese and control mice by abdominal injection for 5 weeks. Obese mice were fed a diet high in fat, sugar and cholesterol for 24 weeks leading up to treatment.
“The treated mice completely lost the weight gain and had no adverse side effects.” To tell Tayumanavan.
The mice remained on the diet throughout the treatment, and not only did their weight return to normal, but their cholesterol levels dropped and harmful levels of liver inflammation subsided.
“We found that it activates the reverse cholesterol transport pathway that lowers cholesterol,” says Tayumanabhan. To tell.
“We believe that activation of fat oxidation and increased metabolic rate are responsible for weight loss, but further research is needed to prove this point.”
After ANG enters hepatocytes, the axitilome is released when the intrahepatocyte environment disrupts the bonds within the nanogel. The drug then binds to proteins that help regulate gene expression.
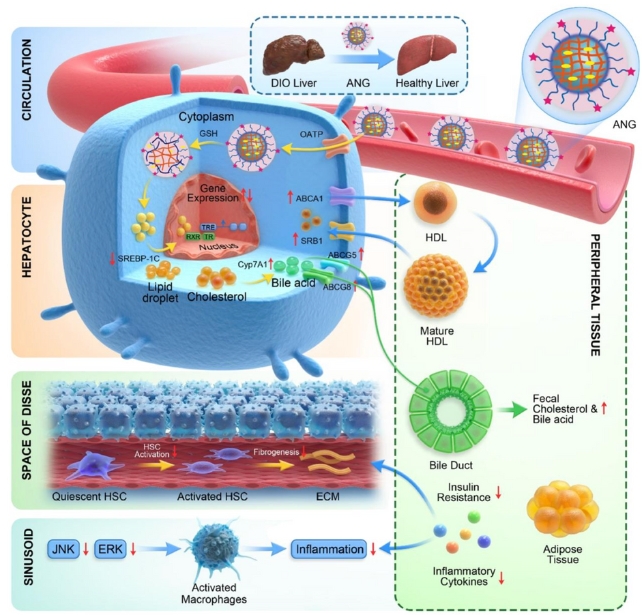

The ability of axitilome delivered by ANG to reverse weight gain without causing widespread changes in thyroid hormone levels suggests the potential of thyromimetics in the treatment of metabolic diseases such as obesity, a major public health problem. are doing.
The axitilome-fed mice maintained an appetite for a continuous high-density diet, which is noteworthy, the authors say. This contradicts observations of humans using another class of drugs for weight loss.
“A huge amount of development work has to be done between mice and humans,” says Tayumanavan. To tell“But we expect it to end up being a drug.”
Tayumanavan co-founded a start-up based on nanogel technology developed in his lab. Cyta TherapeuticsOne of its main objectives is to develop innovative delivery platforms to bring the right drugs to the right places in the body.
This research PNAS Nexus.